All about the idea funnel
Reading time: about 6 min
An idea funnel is a tool used to determine which ideas are most advantageous to the business. It’s a visualization technique that is most commonly used to help companies understand what new ideas are realistic and worth moving forward with. This is invaluable because, while an idea may be very good, it might not be the best for the market, the business, or the moment in time. The idea funnel helps to sort and prioritize the best ideas.
If you’ve ever come across a new product in a store and thought, “That’s a great idea,” you might have just assumed the product arose from a flash of brilliance. Perhaps that’s true, but it’s more likely that the product is the result of a great deal of deliberation and strategy. After all, consider how many ideas arose from a recent brainstorming session you’ve had. Multiply those ideas by hundreds or even thousands, and you’ll start to understand just how overwhelming it can be to determine which ideas are worth pursuing and which should be ignored.
Businesses need a strategic way to sift through ideas and pinpoint those that are most beneficial to the bottom line and to their growth. That’s where the idea funnel comes in.
What is an idea funnel?
An idea funnel is a tool used to determine which ideas are most advantageous to the business. It’s a visualization technique that is most commonly used to help companies understand what new ideas are realistic and worth moving forward with. This is invaluable because, while an idea may be very good, it might not be the best for the market, the business, or the moment in time. The idea funnel helps to sort and prioritize the best ideas.
This powerful tool—also known as idea modeling or an ideation funnel—is primarily about bringing something new to your organization or customers, but it also helps you brainstorm, refine, and execute the best ideas. So, while you may have just been forming an idea prior to using the idea funnel, you’ll likely have a robust, carefully thought-out idea at the end of the exercise.
Different models for an ideation funnel
There’s no one right way to go about implementing an idea funnel, so explore different options before committing to a model. Here are a few to check out:
Stage-gate method
Also referred to as the “phase-gate process,” this method can be thought of as something like a video game in which sequential stages aren’t “unlocked” until previous requirements are met.
The stages of this process are:
- Discover: The ideation and brainstorming phase
- Scope: A general outline of the project, including an exploration of the project’s goals
- Design: A more detailed examination of the project that involves research, justification, and the development of a business case, metrics, and plans
- Develop: The actual creation of the product or service that will eventually be scaled out for the market
- Scale: Tests and trials, product validation, operations plans, and marketing propositions
- Launch: Introduction to the market, including full production and sales
Each of those five stages is gated by three specific components:
- Input: Examining and evaluating the previous stage’s results
- Criteria: Using data and KPIs to measure against defined success metrics
- Output: Considering the above, the idea is given the go-ahead, killed, recycled, or held off on until a future time
The stage-gate method is a very precise method of moving through the ideation and launch process, but it lacks the creative freedom of other methods.
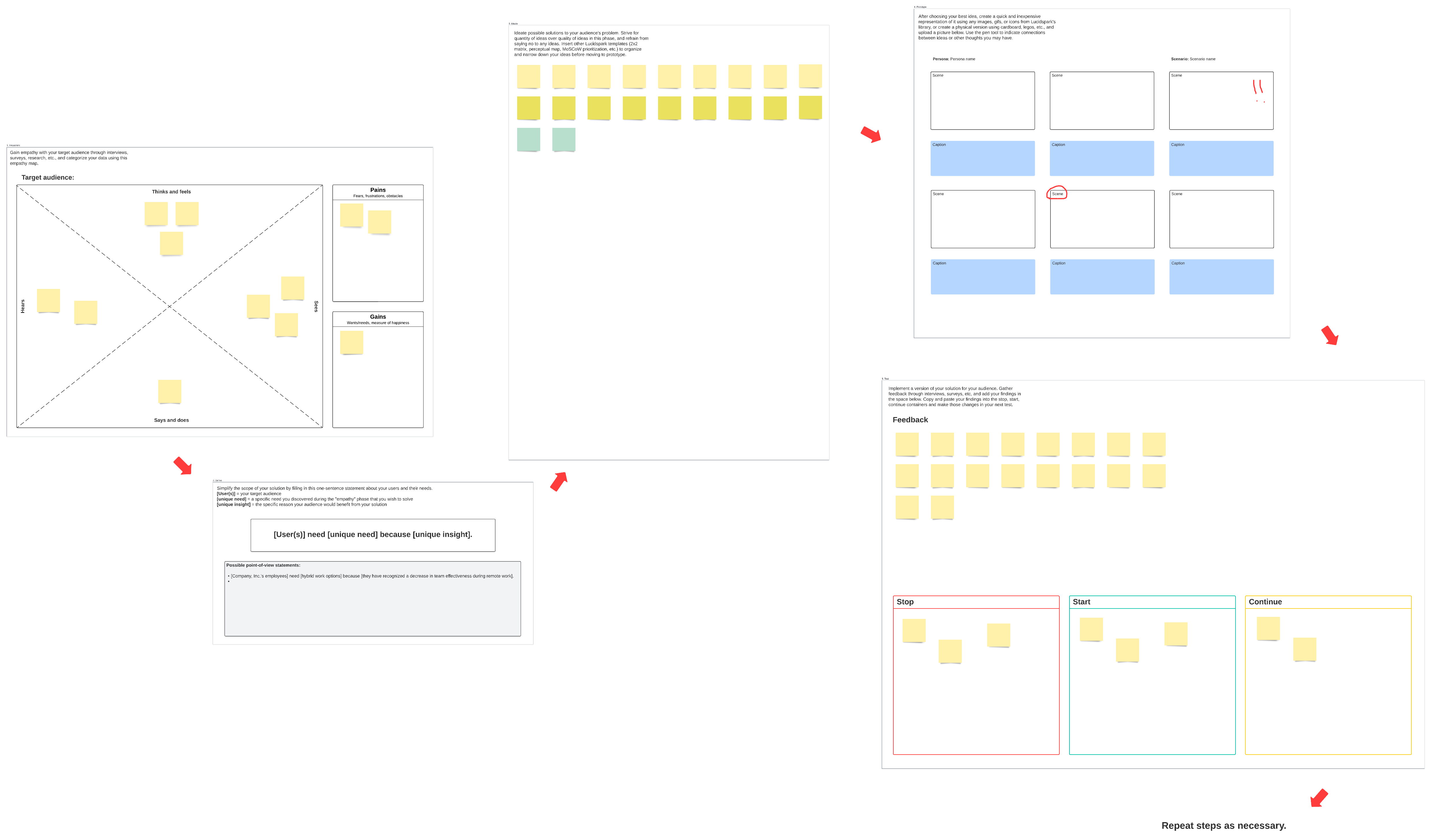
Design Thinking method
This method is nonlinear, meaning your team may start at whichever stage they’d like, run them in parallel, and revisit stages again later. The Design Thinking method consists of five stages:
- Empathize: Put yourself in the shoes of your users and determine what problems they have
- Define: Articulate the needs of your users
- Ideate: Brainstorm ways to meet your users’ needs
- Prototype: Build! Experiment and iterate
- Test: Test the prototypes
While the Design Thinking method encourages creativity, it lengthens the duration of the project overall. If you’re in a time crunch, this may not be the best model to use.
Lean startup method
As the name implies, this method is useful for quickly spinning a startup into reality. Lean startup prioritizes learning and innovation as well as proper management, and it’s useful for minimizing the waste that is common with startups. There are essentially three phases to this method:
- Build: Get a minimum viable product into existence quickly so that it can be tested by actual customers
- Measure: Gathering data is the name of the game here—otherwise, there’s no way to iterate. Gather feedback from customers and collect valuable data that can be incorporated into future models.
- Learn: Go beyond simply gathering and learn from the data and feedback you’ve collected. Determine what’s working and what isn’t.
The lean startup method prioritizes action. This is great for getting a product into the market but not great for minimizing risk. If you need to prioritize speed, this is the method to try out.
Steps to creating an idea funnel
If the above models don’t seem to fit your needs, there are many others to choose from that are essentially composed of the following steps:
- Opportunity assessment: First, analyze what opportunities exist in the market. What have your customers asked for? What do they need? What opportunities are there to expand your product lines or break into a new market?
- Insight based ideation: After pinpointing an opportunity that could be a good fit for your business’s strategy, determine the right kind of product or service that could fill this opportunity. You can brainstorm, use market research, and gather input from online communities and your own customers to help.
- Conceptualization: Once you’ve identified a product or service that will help maximize this opportunity, it’s time to start bringing it to life. Create an MVP (minimum viable product), models, or concepts and begin iterating on them to improve their viability.
- Evaluation and benchmarking: Now, it’s time to see how your customers respond to your idea. Test your product or service on customers. See how the market responds. You may want to iterate again based on this feedback.
- Consolidation: This is the make-or-break part of the process where you decide if the idea is worth continuing to invest in or if it should be scrapped. Making this determination is difficult, but it’s necessary to preserve resources and continue investing in valuable ideas.
- Launch: If your idea makes it past step 5, bring your idea to market! This is where your hard work translates into a viable product that can be used by your customers at scale.
Identifying the right ideas can be difficult. You might have a great idea, but is it right for your business and customers? And how can you even tell the great ideas from the bad ones? The idea funnel can help with all of these questions while also preventing the drain of resources that results from pursuing the wrong idea for too long. Ideas are powerful, but they need to be managed carefully, and sometimes they need several iterations before you realize their true potential.
Supercharge your idea modeling with Lucidspark
Creating an idea funnel can be a complicated process. Utilizing a visual collaboration platform like Lucidspark is a great way to simplify the complex, saving you time (and money) in the end. Easily keep up-to-date documentation and quickly align your team every step of the way using one of our many ideation templates, so none of your best ideas fall through the cracks.

Get started on your own idea funnel.
Go nowAbout Lucidspark
Lucidspark, a cloud-based virtual whiteboard, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This cutting-edge digital canvas brings teams together to brainstorm, collaborate, and consolidate collective thinking into actionable next steps—all in real time. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidspark.com.
